DB) SQL 연습(1)
August 21, 2020
Ddatabase
DDL - 정의어(data definition language) : create , drop, altor
DML - 조작어(data manipuldateion language) : insert, select, update, delete
DCL - 제어어(data control language) : grant revoke
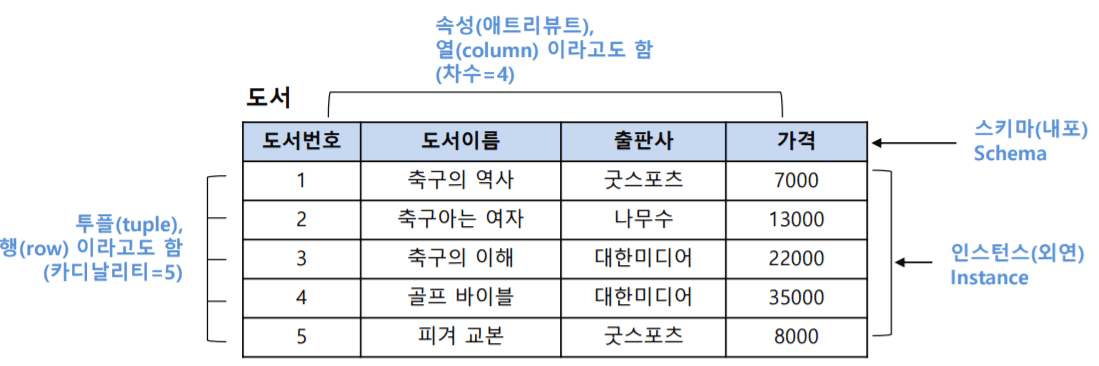
도메인 : 도메인은 동일한 테이블 타입을 가지는 속성을 분리하는 것을 의미
속성 = column = field
record = row = tuple = cadinallity
select 간단예시
select 컬럼 from 테이블 where 조건M:N관계는 보통 만들지 않고 둘을 쪼개서 1:M , 1:N으로 만든다
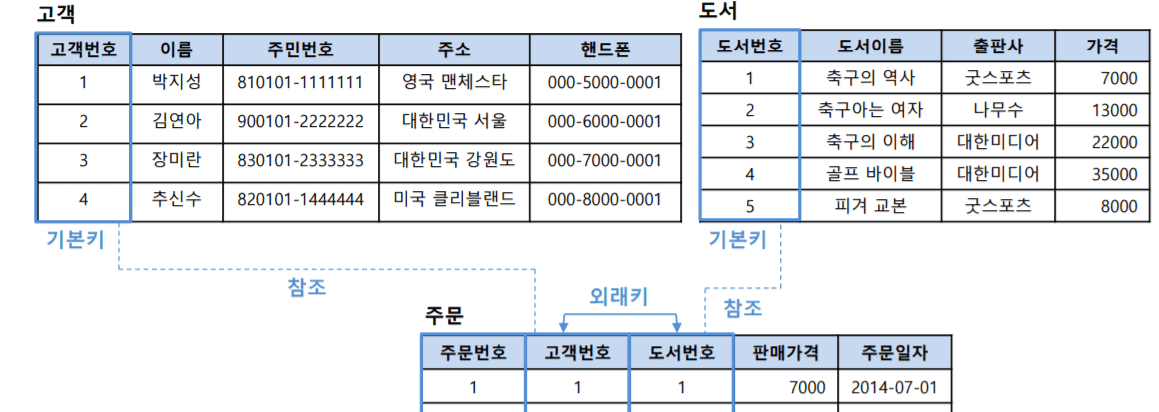

외부조인(p.56) : 주문하지 않은 장미란 데이터도 가져올 수 있다
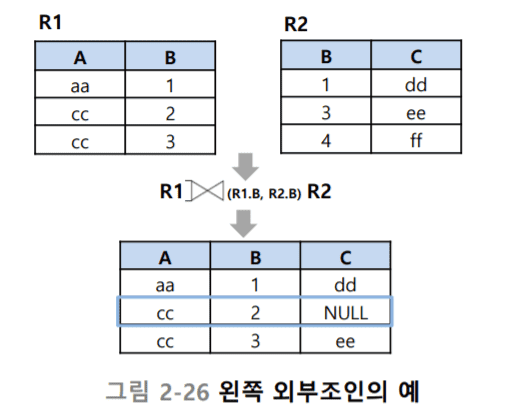
현재 왼쪽 다 표시(left join)
DML
select
select distinct publisher from Book; -- disticnt는 중복 제거where
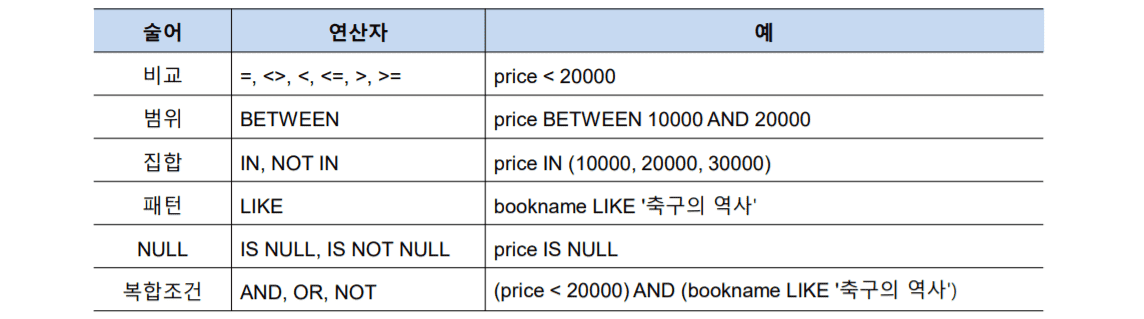
select * from Book where price<20000; -- 가격 20000 아래 모두
# 같은 구문
select * from Book where price between 10000 and 20000;
select * from Book where price >= 10000 and price <=20000;
select * from Book where publisher in('굿스포츠','대한미디어'); -- 포함된
select * from Book where publisher not in('굿스포츠','대한미디어'); -- 포함 안 된
select * from Book where bookname like '축구%'; -- 축구라는 단어 일부가 포함된놈들 검색, 뒤에 % 붙여서 뒤에 아무거나 와도 됨
select * from Book where bookname like '%구%'; -- '구' 앞 뒤로 아무거나 와도 됨
select * from Book where bookname like '축구%' and price>=20000; -- 복합조건Order by
select * from Book order by bookname desc; -- 내림차순 정렬, 디폴트는 오름차순
select * from Book order by publisher asc, price desc; -- 1차로 publisher 정렬, 2차로 desc 내림차순 정렬집계함수
select sum(saleprice) as '총매출' from Orders; -- saleprice 합계를 총매출이란 이름으로 출력
select sum(saleprice), avg(saleprice), count(saleprice), max(saleprice), min(saleprice) from Orders; -- 이런 기능이 있다group by
select custid, count(*), sum(saleprice), avg(saleprice) from Orders group by custid;
-- custid로 그룹을 묶는데, 그 그룹 내에서 전체 카운트, 합계, 평균을 출력*/having (group by 없이는 사용되지 않는다)
select custid, count(*), sum(saleprice)
from Orders where saleprice >= 8000 group by custid
having count(*) >= 2 and sum(saleprice) >= 30000; -- 가격이 8천원 이상인 고객이 구매한 책의 수량, 단 2권 이상 구매한 고객과 3만원 이상인 고객만. 여기서 결과에 대해 조건을 줄 때는 having을 사용Join
-- 이름 기준으로 그룹묶고 오름차순 정렬하고 합계출력인데, 고객과 주문의 custid가 같아야함
select name, sum(saleprice)
from Customer, Orders
where Customer.custid = Orders.custid
group by Customer.name
order by Customer.name;고객의 이름과 고객이 주문한 도서 이름 중 가격 20000이상인 놈들 출력
select c.name, b.bookname, b.price -- 출력할 속성
from Customer as c, Orders as o, Book as b -- 참조할 테이블
where c.custid = o.custid and o.bookid=b.bookid and b.price >=20000; -- 조건where 의 조건은 on 에 써준다
-- 두 구문은 같은 구문, join쓰고 안 쓰고의 차이
select c.name, o.saleprice
from Customer as c join Orders as o
on c.custid = o.custid
where saleprice >= 20000;
select c.name, o.saleprice
from Customer as c, Orders as o
where c.custid=o.custid and saleprice >= 20000;쿼리 안에 쿼리, 가장 비싼책의 이름을 알고싶다
select bookname from Book
where price=(select max(price) -- 가장 비싼책의 가격을 price에, 그 bookname을 가져오겠다
from Book);한번이라도 구매한적 있는 고객
select name from Customer
where custid in (select custid from Orders);대한미디어 들어가는 책 산 고객
select name from Customer -- 3. 그 id의 이름을 출력
where custid in(
select custid from Orders -- 2. 그걸 구매한 사람의 id를 가져오고
where bookid in(
select bookid from Book where publisher='대한미디어')); -- 1. 대한미디어인 책을 가져오고** 출판사별로 출판사의 평균 도서 가격보다 비싼 도서를 구하시오
select b1.bookname, b1.publisher from Book as b1
where b1.price > (select avg(b2.price) from Book as b2
where b1.publisher=b2.publisher); -- 안의 select에서 group by 할 필요가 없다!DDL
char(10) 는 10개의 배열을 풀로 사용하지만,
varchar(10)은 만약 2개의 배열만 사용했다면 나머지 8개는 지워버려서 효율적이다
create
create table NewBook(
bookid integer not null,
bookname varchar(20) not null,
publisher varchar(20) null,
price integer default 10000,
primary key(bookid) -- 기본키 지정, 안에 쉼표 넣고 키 추가하면 복합키 된다
);
create table NerCustomer(
custid integer primary key,
name varchar(40) not null,
address varchar(40),
phone varchar(15) default '000-0000-0000' -- 값 없으면 디폴트 넣는다
);
-- 이제 참조할 수 있도록 외래키 포함한 테이블 작성
CREATE TABLE NewOrders (
orderid INTEGER,
custid INTEGER NOT NULL,
bookid INTEGER NOT NULL,
saleprice INTEGER,
orderdate DATE,
PRIMARY KEY (orderid),
FOREIGN KEY (custid) REFERENCES NewCustomer(custid) ON DELETE CASCADE
-- FOREIGN KEY (bookid) REFERENCES NewBook(bookid) ON DELETE CASCADE 외래키 이렇게 추가
-- NewCustomer의 custid랑 연동되도록 설정. 연쇄삭제. cascade로 설정하면 부모와 자식에 동시에 영향을 미친다
);
-- ddl은 아니지만 테스트
insert into NewBook values(100, 'Docker', 'SkInfosec', 20000);
insert into NewCustomer values(10, 'jeonghoon', 'seoul', '010-5280-6607');
insert into NewOrders values(1,10,100,30000, now()); -- now는 현재 시간
insert into NewOrders values(2,20,200,30000, now()); -- 얘는들어가지 않는다. 두번째 값인 custid는 외래키, 즉 직접 넣을 때 참조하는 테이블인 NewCustomer에 없는 custid면 생성 불가능
update NewCustomer set custid=20 where custid=10; -- 자식은 부모 테이블 함부러 못바꾼다, update cascade 걸어 놓으면 바꿀 수 있음
delete from NewCustomer where custid=10; -- delete cascade 조건 걸어놨기 때문에 데이터 삭제 가능alter
-- 위 NewBook에서
alter table NewBook add isbn varchar(13); -- isbn이라는 속성 추가
alter table NewBook modify isbn integer; -- 그 속성의 타입 int로 변경
alter table NewBook drop column isbn; -- 속성 제거
alter table NewBook modify bookid integer not null; -- 기존 속성 not null로 변경
alter table NewBook add primary key(bookid); -- 기본키 없을 때 기본키 추가
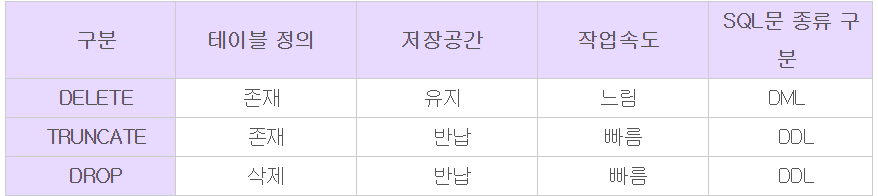
-- 테이블 삭제
drop table NewOrders;
drop table NewBook;
drop table NewCustomer;DML
insert
insert into 테이블이름[(속성리스트 생략가능)] values(값 리스트);
insert into Book(bookid, bookname, publisher, price)
select bookid, bookname, publisher, price from Imported_Book; -- 다른테이블에 있는거 바로 저장 가능
-- 컬럼 수와 null 등의 조건이 맞다면 간단하게 표현 가능
insert into Book
select * from Book;update
update 테이블명 set 속성명 = 값 where 조건;
-- Imported_Book 테이블의 bookid가 21번인 놈의 출판사를 Book테이블의 bookid가 12번 놈으로 바꾸기
update Book set publisher=(select publisher from Imported_Book where bookid=21) where bookid=12;delete
delete from Book where bookid=11; -- 11번 삭제
quiz
-- 1. 박지성의 총 구매액
select sum(o.saleprice) from Orders as o, Customer as c where o.custid=c.custid
-- 2. 박지성이 구매한 도서의 수
select count(bookid)
from Orders
where custid=(select custid from Customer where name='박지성');
-- 3. 박지성이 구매한 도서의 출판사 수
select count(b.publisher)
from Book as b, Orders as o
where b.bookid=o.bookid and o.custid = (select custid from Customer where name='박지성');
-- 4. 박지성이 구매한 도서의 이름, 가격, 정가와 판매가격의 차이
select b.bookname, b.price, b.price-o.saleprice
from Book as b, Orders as o, Customer as c
where b.bookid=o.bookid and o.custid=c.custid and name like '박지성';
-- 5. 박지성이 구매하지 않은 도서의 이름
select b.bookname
from Book as b, Orders as o
where b.bookid=o.bookid and o.custid <> (select custid from Customer where name='박지성');
-- 6. 2014년 7월 4일~7월 7일 사이에 주문받은 도서의 주문번호
select * from Orders
where orderdate between '2014-07-04' and '2014-07-07';
-- 7. 2014년 7월 4일~7월 7일 사이에 주문받은 도서를 제외한 도서의 주문번호
select * from Orders
where orderdate not between '2014-07-04' and '2014-07-07';
-- 8. 고객의 이름과 고객이 구매한 도서 목록
-- 9. 도서의 판매액 평균보다 자신의 구매액 평균이 더 높은 고객의 이름
select name ,avg(saleprice)
from Customer as c, Orders as o
where c.custid=o.custid
group by name
having avg(saleprice) > (select avg(saleprice) from Orders);
-- 10. 박지성이 구매한 도서의 출판사와 같은 출판사에서 도서를 구매한 고객의 이름
-- 11. 두 개 이상의 서로 다른 출판사에서 도서를 구매한 고객의 이름
select name from Customer as c1
where 2 >= (
select count(distinct publisher) from Customer as c, Orders as o, Book as b
where c.custid=o.custid and o.bookid=b.bookid and (name like c1.name)
);
-- 12. 전체 고객의 30% 이상이 구매한 도서
select bookname from Book as b1
where (
select count(b.bookid)
from Book as b, Orders as o
where b.bookid=o.bookid
and b.bookid=b1.bookid)>=0.3*(select count(*) from Customer);quiz2
-- 1. 팀장(manager)의 이름을 보이시오.
select name from Employee where position='Manager';
-- 2. ‘IT’ 부서에서 일하는 사원의 이름과 주소를 보이시오.
select name, address from Department as d, Employee as e
where d.deptno=e.deptno and d.deptname='IT';
-- 3. ‘홍길동’ 팀장(manager) 부서에서 일하는 사원의 수를 보이시오.
select count(deptno) from Employee
where deptno=(select deptno from Employee where name='홍길동');
-- 5. 두 명 이상의 사원이 참여한 프로젝트의 번호, 이름, 사원의 수를 보이시오.
select p.projno, p.projname, count(name) from Employee as e, Project as p
where e.deptno=p.deptno
group by p.projno, p.projname
having count(*) >=2;
-- 6. 세 명 이상의 사원이 있는 부서의 사원 이름을 보이시오.
select e.name from Employee as e, Department as d
where e.deptno=d.deptno and d.deptname=(
select deptname from Employee as e, Department as d
where e.deptno=d.deptno
group by d.deptname having count(name) >=3);